Rails
The rails_semantic_logger gem replaces the default Rails logger with Semantic Logger.
It also reduces Rails logging output in production to almost a single line
for every Controller-Action call.
Rails Support
For the complete list of supported Ruby and Rails versions, see the Testing file.
Installation
Add the following lines to Gemfile
gem "amazing_print"
gem "rails_semantic_logger"
The gem amazing_print is optional, but is recommended to get colorized output of semantic data
(Hash output).
Install required gems with bundler
bundle install
This will automatically replace the standard Rails logger with Semantic Logger which will write all log data to the configured Rails log file.
Conflicting Gems
Remove all of the following gems since they conflict or duplicate what Rails Semantic Logger already achieves.
- lograge
- rails_stdout_logging
- rails_12factor
Process Forking
See Process Forking if you use Unicorn or Puma.
Heroku
Log to standard out.
When running on Heroku all logging needs to be set to standard out.
Add the following to config/environments/production.rb:
if ENV["RAILS_LOG_TO_STDOUT"].present?
$stdout.sync = true
config.rails_semantic_logger.add_file_appender = false
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(io: $stdout, formatter: config.rails_semantic_logger.format)
end
Heroku sets the RAILS_LOG_TO_STDOUT environment variable to true.
Setting the log level.
The log level is usually set with the config setting config.log_level, but
Heroku also allows the log level to be set via the LOG_LEVEL environment variable.
heroku config:set LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG
To enable the above log level environment variable for Heroku, add the following to config/environments/production.rb:
if ENV["LOG_LEVEL"].present?
config.log_level = ENV["LOG_LEVEL"].downcase.strip.to_sym
end
Configuration
The configuration can be set in either config/application.rb or the environment specific file in
config/environments.
Standard Rails log output for a single page request
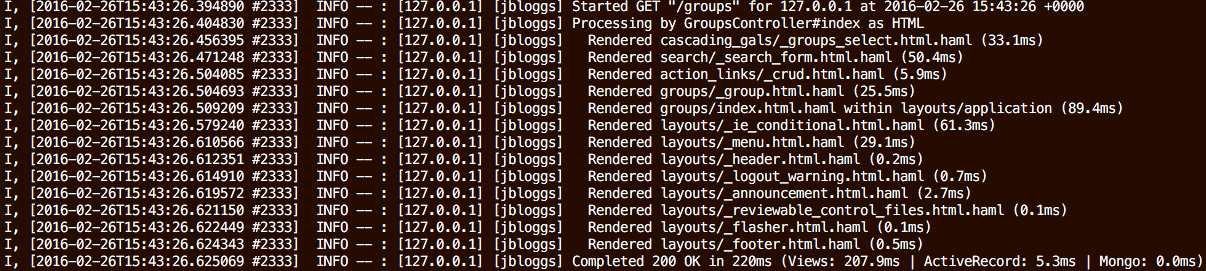
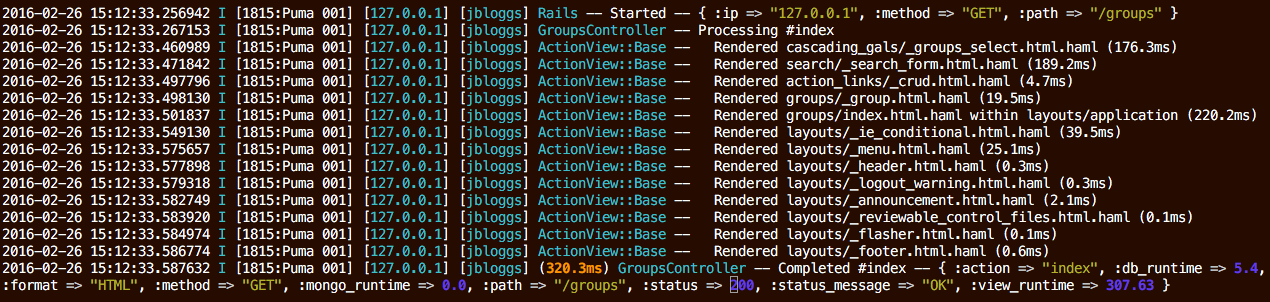
Rails log output for the same single page request after adding the rails_semantic_logger gem:

Re-enable Started, Processing, and Rendered messages
config.rails_semantic_logger.started = true
config.rails_semantic_logger.processing = true
config.rails_semantic_logger.rendered = true
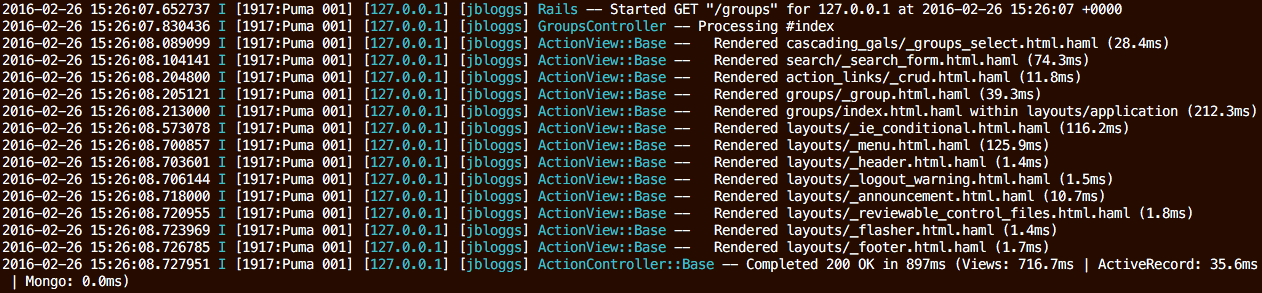
Original Rails messages with semantic logger formatting
config.rails_semantic_logger.semantic = false
config.rails_semantic_logger.started = true
config.rails_semantic_logger.processing = true
config.rails_semantic_logger.rendered = true
Include the file name and line number in the source code where the message originated
Warning: Either set this to nil (to disable it completely) or to a high log level (:fatal or :error) in your production environment otherwise you risk encountering a memory leak due to the very high number of
objects allocated when Ruby backtraces are created. This is best used in development for debugging purposes.
config.semantic_logger.backtrace_level = :info

The above output shows 3 web requests where the source file name was log_subscriber.rb and line number 11.
Log Level
To change the log level:
# Set to the log level to :trace, :debug, :info, :warn, :error, or :fatal
config.log_level = :debug
To change the log level when running inside of a running Rails console:
SemanticLogger.default_level = :debug
Named Tags
Named tags can be added to every log message on a per web request basis, by overriding the Rails built-in
config.log_tags with a hash value.
For example, add the following to application.rb, or replace the existing config.log_tags entry:
config.log_tags = {
request_id: :request_id,
ip: :remote_ip,
user: -> request { request.cookie_jar["login"] }
}
Note:
- If a value returns nil, that key and value will be left out of the named tags for that request.
:request_idabove is for Rails 5 and above. With Rails 4.2 use:uuid
To turn off named tags in development, add the following to config/environments/development.rb
config.log_tags = nil
Rails Console Logging
By default the Rails Semantic Logger adds a logger to stderr when running inside a rails console.
To disable this behavior:
config.rails_semantic_logger.console_logger = false
Quiet asset logging
Rails logs asset retrievals at the debug level. These log entries can quickly clutter the log output:
Rack -- Started -- {:ip => "127.0.0.1", :method => "GET", :path => "/assets/rocket_job_mission_control/rocket-icon-64x64.png"}
To turn off the asset logging:
config.rails_semantic_logger.quiet_assets = true
Colorize Logging
If the Rails colorized logging is enabled, then the colorized formatter will be used by default. To disable colorized logging in both Rails and Semantic Logger:
config.colorize_logging = false
Semantic log output
By default Action Controller and Active Record text messages are converted to semantic data (Hash):
Rack -- Started -- { :ip => "127.0.0.1", :method => "GET", :path => "/users" }
UserController -- Completed #index -- { :action => "index", :db_runtime => 54.64, :format => "HTML", :method => "GET", :mongo_runtime => 0.0, :path => "/users", :status => 200, :status_message => "OK", :view_runtime => 709.88 }
To disable semantic message conversion:
config.rails_semantic_logger.semantic = false
Started message
By default the Started message is logged at the debug level so that it does not appear in production.
Rack -- Started -- { :ip => "127.0.0.1", :method => "GET", :path => "/users" }
To show Rack started messages in production:
config.rails_semantic_logger.started = true
Processing message
By default the Controller Processing message is logged at the debug level so that it does not appear in production.
UserController -- Processing #index
To show the Controller Processing message in production:
config.rails_semantic_logger.processing = true
View Rendering messages
By default the Action View rendering messages are logged at the debug level so that they do not appear in production.
ActionView::Base -- Rendered data/search/_user.html.haml (46.7ms)
To show the Action View rendering messages in production:
config.rails_semantic_logger.rendered = true
Amazing Print Options
The default Amazing Print options can be changed by supplying any valid Amazing Print options:
config.rails_semantic_logger.ap_options = {multiline: false}
The defaults can also changed be creating a ~/.aprc file.
See the Amazing Print Documentation
Notes:
- The option
:multilineis set to false if not supplied. - Has no effect if Amazing Print is not installed.
Additional appenders
Example, also log to a JSON log file, for consumption by ELK, Splunk, etc.:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(file_name: "log/#{Rails.env}.json", formatter: :json)
Example, also log to a local Syslog:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(appender: syslog)
Example, also log to a local Syslog such as syslog-ng over TCP:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(appender: syslog, url: "tcp://myloghost:514")
Example, also log to elasticsearch:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(appender: :elasticsearch, url: "http://localhost:9200")
Example, also log to BugSnag:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(appender: :bugsnag)
See Appenders for the complete list of available appenders.
Output Format
The Rails log file and Rails Server standard out logging can be modified directly with the format config option.
config.rails_semantic_logger.format = :default
Valid options:
- :default
- Plain text output with no color.
- :color
- Plain text output with color.
- :json
- JSON output format.
- :logfmt
- logfmt output format.
- :one_line
- Reduce each log message to a single line.
-
ObjectAn instance of any class that derives fromSemanticLogger::Formatters::Base. ProcA block that will be called to format the output. It is supplied with thelogentry and should return the formatted data.
Note:
:defaultis automatically changed to:colorifconfig.colorize_loggingis notfalse.
JSON Example, in application.rb:
config.rails_semantic_logger.format = :json
Custom Example, create app/lib/my_formatter.rb:
# My Custom colorized formatter
class MyFormatter < SemanticLogger::Formatters::Color
# Return the complete log level name in uppercase
def level
"#{color}log.level.upcase#{color_map.clear}"
end
end
In application.rb:
config.rails_semantic_logger.format = MyFormatter.new
See SemanticLogger::Formatters::Color for the other methods that can be overridden.
To modify and use a different base formatter choose from the complete list of formatters.
Disable default Rails file logging
When running in an environment where local file logging is not available, or to completely replace the file logger, disable the default rails file logging by setting:
config.rails_semantic_logger.add_file_appender = false
After disabling the default file logging another appender needs to be added before any logging will be sent anywhere. For example to create a JSON only log file:
config.semantic_logger.add_appender(file_name: "log/json.log", formatter: :json)
Notes:
- If the default file logger is not used then any logging failures will be written to stderror.
- When running the Rails server, it automatically adds an appender that logs to standard out.
- To disable the Rails server standard out logging add the following option when starting it from the command line:
bin/rails s --daemon
- Or if running Puma, add the
--quietoption.
- To disable the Rails server standard out logging add the following option when starting it from the command line:
- It is usually a good idea to turn off standard out logging in production.
Adding custom data to the Rails Completed log message
During Controller-action processing custom data can be added to the Rails Completed message.
Add a method called append_info_to_payload to the controller to modify the payload that is logged:
class ThingController
private
def append_info_to_payload(payload)
super
payload[:user_id] = 42
end
end
Log file name and line number
In development to log the file and line number from which every log message originated:
# Log file name and line number for log messages at this level and above
config.semantic_logger.backtrace_level = :debug
By default backtraces are only captured for :error and :fatal levels since capturing a backtrace
for every log message is expensive.
This feature can be used in production, but use with care since setting the level too low will slow down the application.
Custom Controller Base Class
If your application is using a custom controller base class other than ActionController::Base or ActionController::API,
then Rails Semantic Logger will fall back to the ActionController::Base logger instance.
This is not ideal since all log entries from that controller will now have the name ActionController::Base.
To make the log entries use the correct class name add the following to your custom controller class:
include SemanticLogger::Loggable
Or, if the custom controller base class is inside of a third party gem, add an initializer with:
CustomControllerBase.include(SemanticLogger::Loggable)
Where CustomControllerBase is the name of the custom controller base class.
Log Rotation
Since the log file is not re-opened with every call, when the log file needs to be rotated, use a copy-truncate operation over deleting the file.
Sample Log rotation file for Linux:
/var/www/rails/my_rails_app/shared/log/*.log {
daily
missingok
copytruncate
rotate 14
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
}
Replacing Existing loggers
Rails Semantic Logger automatically replaces the default loggers for the following gems after they have been initialized:
- Bugsnag
- Mongoid
- Mongo
- Moped
- Resque
- Sidekiq
- Sidetiq
- DelayedJob